Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Saegusa, Hiromitsu; Takeuchi, Ryuji; Oyama, Takuya; Takeuchi, Shinji
no journal, ,
One of the main goals of the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory project is to establish comprehensive techniques for investigation, analysis, and assessment of the deep geological environment. In Phase I, hydrogeological investigations have been carried out in a stepwise manner in order to obtain information on important parameters. Hydrogeological modeling and groundwater flow simulation to evaluate the uncertainty of the hydrogeological model and to identify the main issues for further investigations. In Phase II, long-term hydraulic monitoring, which is for mainly determined and assessed hydraulic response during excavation of MIU, geological mapping and hydraulic testing using boreholes drilled from underground tunnels have been also carried out. Based on the results of the field investigations, hydrogeological model constructed in Phase I has been tested and revised. These results will be introduced.
Hashimoto, Shuji*; Saegusa, Hiromitsu; Tanaka, Tatsuya*; Ando, Kenichi*; Bruines, P.*
no journal, ,
It is useful to estimate profiles of the equivalent hydraulic conductivity for groundwater flow modeling based on an equivalent porous medium approach that are used for hydrogeological characterization at over the several kilometers scale. In this study, a combined interpretation of core observations, BTV and fluid logging has been used to identify and classify water-conducting features (WCFs) among observed fractures in deep boreholes around the MIU construction site in Phase I. Transmissivity profiles of WCFs were determined by the interpretation of fluid logging and the results of short interval packer tests. An equivalent hydraulic conductivity for the sub-divided block is calculated using a hydraulic discrete fracture network (hydroDFN) model based on the information, and is confirmed the validity using long interval packer test results. Groundwater flow analyses using developed hydroDFN model are also carried out to assess groundwater flow conditions around galleries.
Hanamuro, Takahiro; Umeda, Koji; Maeda, Katsuhiko*
no journal, ,
Although no evidence of volcanism during the Pliocene and Quaternary is known in the Kii Peninsula, it has long been recognized to be several hot springs with discharge temperatures higher than 60  C. On the other hand, several tens of small-scale vein-type metal deposits are distributed around the southern part of Kii Peninsula, whose heat source are thought to be Middle Miocene acidic magmatism associated with Kumano Acidic Rocks. The results of the dating of altered rocks from these hot spring area, ore deposits and their surroundings altered rocks show that high temperature hydrothermal alteration related to the acidic magmatism occurred in the Middle Miocene, and relatively low temperature alteration has been caused since the Pliocene in Hongu and Totsukawa area. Chemical and isotope data were obtained for fluid inclusions trapped in hydrothermal minerals in the peripheral parts of the high-temperature hot springs, and other vein-type ore deposits. The former inclusions have very low temperatures and low salinities. On the other hand, the latter inclusions are characterized by high temperature fluid with high salinity. The
C. On the other hand, several tens of small-scale vein-type metal deposits are distributed around the southern part of Kii Peninsula, whose heat source are thought to be Middle Miocene acidic magmatism associated with Kumano Acidic Rocks. The results of the dating of altered rocks from these hot spring area, ore deposits and their surroundings altered rocks show that high temperature hydrothermal alteration related to the acidic magmatism occurred in the Middle Miocene, and relatively low temperature alteration has been caused since the Pliocene in Hongu and Totsukawa area. Chemical and isotope data were obtained for fluid inclusions trapped in hydrothermal minerals in the peripheral parts of the high-temperature hot springs, and other vein-type ore deposits. The former inclusions have very low temperatures and low salinities. On the other hand, the latter inclusions are characterized by high temperature fluid with high salinity. The  He/
He/ He ratios of the former inclusions indicate relatively high values, generally in agreement with those of the present-day hydrothermal fluids, resulting in a significant contribution of deep source gases.
He ratios of the former inclusions indicate relatively high values, generally in agreement with those of the present-day hydrothermal fluids, resulting in a significant contribution of deep source gases.
Yamada, Kunimi; Hanamuro, Takahiro; Tagami, Takahiro*; Takagi, Hideo*; Shimada, Koji; Umeda, Koji; Iwano, Hideki*; Danhara, Toru*
no journal, ,
Japan Atomic Energy Agency have jointly set up the system of the (U-Th)/He dating in cooperation with Kyoto University and National Institute for Earth Sciences and Disaster Prevention. Through this two years, helium extraction machine using an electronically-cooled diode laser, micro crusible system using XRF bead sampler and uranium and thorium quantification procedure without artificial spikes are developed. Now we produce new ages of some age known samples. At the present stage, the accuracy and precision are roughly 20 and 10%, respectively, using the age standard zircon from the Fish Canyon Tuff (FC3). In the presentation, we will introduce our systems and the ages detailedly.
Katata, Genki; Nagai, Haruyasu
no journal, ,
A new methodology to evaluate an index of Water Sustainability for Vegetation (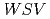 ) is proposed.
) is proposed. 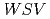 is defined as the ratio of water supply (considering rainfall, surface runoff and fog deposition on vegetation) to demand (evapo-transpiration) by vegetation. Simulations using a mesoscale meteorological model (MM5) were employed to make meteorological fields. At each simulation grid, fog deposition and
is defined as the ratio of water supply (considering rainfall, surface runoff and fog deposition on vegetation) to demand (evapo-transpiration) by vegetation. Simulations using a mesoscale meteorological model (MM5) were employed to make meteorological fields. At each simulation grid, fog deposition and 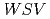 were quantified by a detailed land surface model (SOLVEG) for several vegetation species. This method was applied to develop the high spatial resolution (6 km) maps of fog deposition and
were quantified by a detailed land surface model (SOLVEG) for several vegetation species. This method was applied to develop the high spatial resolution (6 km) maps of fog deposition and 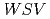 at arid areas in West Asia. At the coastal highland areas along the Red Sea, trees captured a large amount of fog water (60 mm yr
at arid areas in West Asia. At the coastal highland areas along the Red Sea, trees captured a large amount of fog water (60 mm yr ; 30 % of precipitation). The potential vegetation map derived from
; 30 % of precipitation). The potential vegetation map derived from 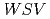 corresponded to the current vegetation map. The proposed method is effective to evaluate water availability for plants surviving under the arid environment.
corresponded to the current vegetation map. The proposed method is effective to evaluate water availability for plants surviving under the arid environment.